It has been said that history repeats itself. This is perhaps not quite correct; it merely rhymes.
Theodor Reik
The chart above is licensed under the CC BY 4.0 license.
It may be shared freely with appropriate attribution.
It has been said that history repeats itself. This is perhaps not quite correct; it merely rhymes.
Theodor Reik

The chart above is licensed under the CC BY 4.0 license.
It may be shared freely with appropriate attribution.
Large numbers are hard to understand. For example, consider this number: 63,000,000. Sixty-three million. How can we put a number like that into perspective? One common technique is to put the number into the context of something more comprehensible.
If you had 63 million 12-ounce bottles of Aquafina water, you could fill up almost nine Olympic-sized pools.
63 million miles is about two-thirds of the average distance from the Earth to the sun. It’s about 264 times further than the average distance from the Earth to the moon.
63 million inches would be 5.25 million feet—about a thousand miles.
If you had 63 million gallons of gasoline, that would enough for half a million people to drive from San Francisco to New York (assuming their cars get 25 miles-per-gallon).
Listen to Scott Bradford reading this essay.
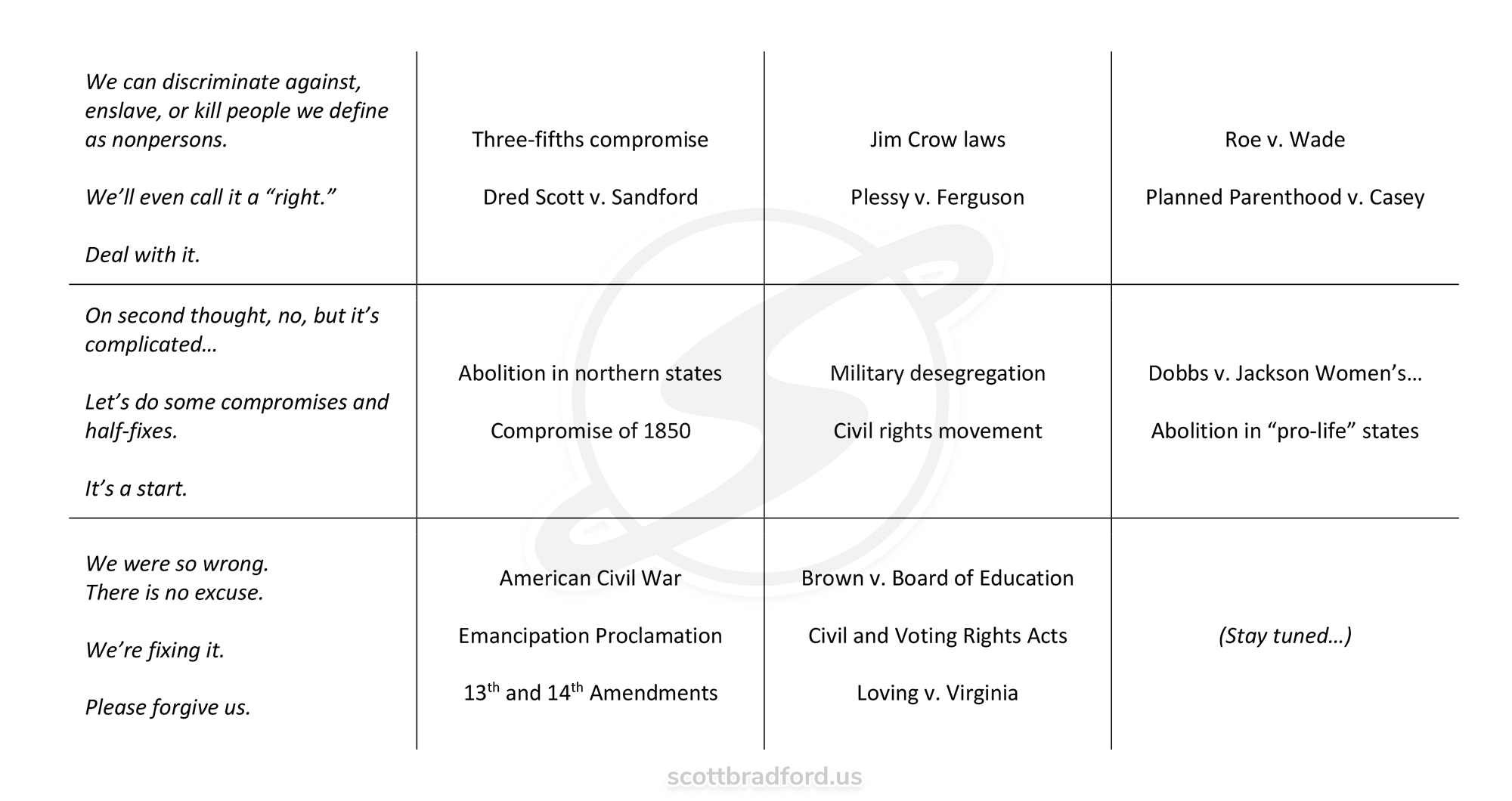
America’s original sin was chattel slavery. It was a reprehensible, inexcusable, indefensible institution that stained most of our first century as a nation and continued to have repercussions for much of a second century after that.
In the 1770s and 1780s, as we were moving from colonial subjugation into our new constitutional republic, the people that built our nation—the founders—wrote beautiful, timeless words about human rights and freedom. These are words that I live by today. And yet there was an inescapable contradiction: Some of the most illustrious of those founders—George Washington, Thomas Jefferson, James Madison, Patrick Henry, and Benjamin Franklin—owned slaves.
They spoke and wrote eloquently about freedom while claiming to own other human beings.
These men, and others like them, cannot be wholly condemned. Like everyone else, they were products of their time who often failed to live up to their own principles. In the grand Christian tradition, I acknowledge that everybody is a sinner. Everybody is a failure. Everybody falls short of the ideal. My own shortcomings seem significantly smaller than those of the people who thought they owned other people, but they aren’t. I am, in my own ways, as reprehensible as they are. This is the reality of our flawed, broken existence.
The United States Supreme Court has overturned Roe v. Wade, the 1973 decision that legalized abortion-on-demand with minimal restrictions throughout the United States. It also overturned Planned Parenthood v. Casey, a 1992 decision that upheld Roe.
In the landmark case of Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health, the court ruled 5-1-3 that there was no justification for taking this issue out of the hands of state legislatures, and that the U.S. Constitution does not protect a so-called right to abortion. The effect of this ruling will be to return the issue to the states. It is likely that there will now be a patchwork of differing legal statuses for abortion across the United States, with some states imposing few (if any) restrictions and others essentially outlawing it.
The court has not ruled on the legality of abortion itself, which is a violation of the fundamental human right to life under natural law and must be prohibited in most cases by just governments. It does, however, open the door for state legislatures to reassert and protect this right.
The majority opinion in this case was written by Justice Samuel Alito, joined by Justices Amy Coney Barrett, Neil Gorsuch, Brett Kavanaugh, and Clarence Thomas. Justices Kavanaugh and Thomas each issued concurring opinions. Chief Justice John Roberts issued an opinion concurring only in the judgment. Justices Stephen Breyer, Elana Kagan, and Sonia Sotomayor issued a jointly-authored dissenting opinion.
I like baseball, in theory. But let’s be honest. The game is sort-of boring. Here are ten things we can do to fix that:
Scott Bradford is a writer and technologist who has been putting his opinions online since 1995. He believes in three inviolable human rights: life, liberty, and property. He is a Catholic Christian who worships the trinitarian God described in the Nicene Creed. Scott is a husband, nerd, pet lover, and AMC/Jeep enthusiast with a B.S. degree in public administration from George Mason University.